Research on Mars has advanced tremendously in the last 20+ years. Precision drives by maxon motors have made an important contribution in these advancements. In four missions by the US space authority NASA, products of the Swiss company have reached the surface of Mars. Data collected during these projects, in part thanks to maxon motors for Mars rovers, bring us closer to the goal of a manned mission to Mars. Additionally, the data gathered from these missions has allowed maxon motors to further improve their products here on Earth.
Mars Exploration
Mars rovers explore the barren landscape of the planet, investigate rock samples, and take breathtaking photos. The rovers of note include Sojourner, Spirit and Opportunity, Curiosity, and Phoenix.
The First Successful Mars Rover: Sojourner
Sojourner was the first rover to land on Mars on July 4, 1997. It was small, weighing only 1.5 kg and equipped with six wheels. Sojourner roamed Mars for almost three months, sending back imagery and data. The vehicle was driven by electrical maxon DC motors with ironless windings installed in the wheels. These motors were used for steering as well as operation of scientific equipment.
The Twin Mars Rovers: Spirit and Opportunity
Spirit and Opportunity were twin rovers sent to Mars that were much larger than their predecessors, weighing around 185 kg each. Equipped with more advanced technology, they were able to take photos, brush and scrape rocks, with the sole mission to find evidence that there used to be water, and potentially life, on Mars. The expected service life for these two rovers was 3 months each. Spirit surpassed these expectations, roaming Mars and sending signals for 6 years before sending its last transmission.
Opportunity was still operational at its 10-year anniversary, traveling more than 40 km. The maxon motors aboard Opportunity were also performing reliably at the 10-year mark. Each rover was equipped with 35 of these precision drives that drive the wheels, steering mechanisms, the RAT (rock abrasion tool), robotic arm, and the cameras. 8 additional maxon motors were used in the lander. In 2014, Opportunity successfully completed its mission, finding traces of water in rock formations in the Endeavor crater.
Mars Rover: Phoenix
The Phoenix rover landed on Mars in 2008 with the mission of scraping away soil at the surface. In doing so, Phoenix revealed bright water ice below. Maxon had supplied 9 RE series precision drives for Phoenix. These drives were designed with special ball bearings to deploy the solar panels on Phoenix.
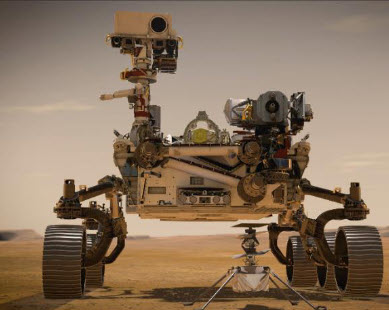
Mars Rover: Curiosity
Curiosity was the biggest Mars rover at its time, weighing nearly 900 kb and being the size of a compact car. Curiosity landed on Mars in 2012 equipped with a robotic arm that can drill and deliver samples to an onboard laboratory. Maxon encoders enabled control of the motors in the electromechanical joints of the rover. During its mission, Curiosity discovered elements such as hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen, the so-called building blocks of life. This discovery further emphasized the possibility of life having once existed on Mars.
The Role of Maxon Motors
In each of the aforementioned Mars rovers, maxon motors were utilized. From steering and cameras, to robotic arm and rock abrasion tools, maxon motors played an integral part in the rovers’ missions. Electromate supplies maxon motors like those used for the Mars rover missions. Contact us today to learn more.